관련뉴스
전문가들이 제공하는 다양한 정보
What NOT To Do When It Comes To The Wood Burning Fire Industry
작성자 작성자 Pamela · 작성일 작성일24-09-22 16:25 · 조회수 조회수 5
페이지 정보
본문
The Dangers of a Wood Burning Fire
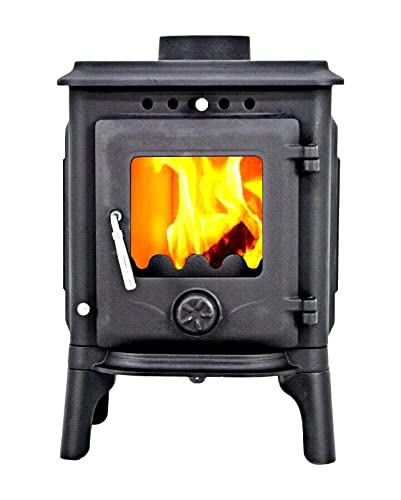 A wood burning fire can offer a warm and enjoyable experience. However, it can also create harmful combustion products. It is essential to know about the way that wood burns and how to utilize your fireplace.
A wood burning fire can offer a warm and enjoyable experience. However, it can also create harmful combustion products. It is essential to know about the way that wood burns and how to utilize your fireplace.
Choose mature logs or kiln dried logs. Logs that are seasoned are less moist and burn hotter than unseasoned logs.
Burning Time
Burning wood to produce heat is a common and efficient method of heating. However, it can release outdoor and indoor emissions that are dangerous to the health of humans. Skillful use of a well-designed fireplace can help reduce the negative effects of burning wood.
The length of time that a wood fire lasts depends on how hot it is. The temperature of the fire will influence the amount of smoke that is produced and the amount of carbon monoxide released. Carbon monoxide can cause occupants to be unable to escape a building that is burning if the levels are too high. It is essential to maintain the temperature of the fire at a lower level the fire to avoid this.
In the initial stage of a wood fire volatile gases such as methane and Methanol are released from the cellulose of the wood. These gases are combustible and non-combustible depending on the moisture levels and the pyrolysis temperature of the sample. The temperature of pyrolysis increases to around 320 degrees Celsius. At this point the cellulose begins to break down and forms charcoal and tar. This process is referred to as wood pyrolysis.
Burning wood releases other toxic combustion products such as dioxins, polyaromatic hydrocarbons, and PAHs. PAHs are known to cause cancer and other illnesses in humans and animals. They can also contaminate soil and water. The wood must be burned in a space that is well ventilated to limit the effects of PAHs.
A wood stove that has an extended burn feature can sustain visible flames for hours while consuming a minimum of fuel. This method of burning involves laying the wood with lighter kindling and larger logs to keep the fire from burning too quickly. This method can be used to achieve the appearance of a fire that produces high temperatures for use over the night or while you are at work.
The duration of a fire is determined by various factors, including the amount of moisture in the wood. Dry wood will have a slower burning time than damp wood. The surface's absorptivity affects its burning time. Simms [59] discovered that the critical heat flux needed to ignite mahogany and oak samples was significantly lower for coated surfaces than those without.
Temperature
The temperature of a fire is incredibly crucial. The temperature of a fire will affect how quickly it burns and also the amount of heat it produces. It also affects the danger when someone is burned. It can also impact how much smoke is produced. If there is a lot of smoke, it can irritate the throat and eyes which is why people should avoid breathing it in.
When wood burns it produces plenty of heat and can even reach high temperatures. The temperature of a fire will differ based on the type of wood that is used and the moisture content. Wet wood, for example is likely to burn at less heat than dry shed wood burning stove. Wet wood absorbs more water, and therefore produces less heat. It is essential to burn dry wood. You should also make sure that the wood has been seasoned before burning.
When the wood reaches a high-burning temperature, a large amount of heat and ash will be released. The amount of ash that is released will be based on the type of wood that is being burned and the heat at which it burns. Certain woods like oak and larch produce very small amounts of ash. The Birch wood can produce a large amount of Ash.
When the wood starts to burn it will go through a three-stage process referred to as pyrolysis. The process begins with the chemical reaction that transforms organic compounds present in the wood into methane and carbon dioxide. The resulting gases are then absorbed by the surrounding air. The gases will rise when the wood is heated and ignite its surface, creating an ignition that heats the wood until it ignites.
The temperature of a fire that is wood burning can be very high, and can cause damage to surfaces if it comes in contact with them. Avoid touching the fire with bare hands as it could cause serious burns. You can reduce your chance of burning by wearing a pair of gloves and working in a well-ventilated area. A mask is recommended when working around fires that burn wood to avoid inhaling smoke.
Smoke
Smoke from wood burning fires is and a mix of gases and fine particles (also known as particulate matter or PM) that contain harmful air pollutants. PM from wood combustion can contain harmful organic compounds, such as formaldehyde and benzene as well mineral particles such as calcium magnesium and potassium. These particles can cause a variety of health problems, including cancer and respiratory diseases. Smoke from wood can cause people to breathe CO, an odorless, colorless gas that can be deadly in small modern wood stove amounts.
The smoke that comes from the wood fire is mostly due to volatile organic compounds (hydrocarbons) evaporating from the burning material. The smoke also contains some water vapor, which is the byproducts of incomplete combustion (such as creosote) as well as some unburned material known as ash.
When choosing the type of wood that you want to burn in your fireplace or woodstove it is recommended to select firewood that has been seasoned. Logs that have been cut and stored away from the weather and allowed to dry until they have been matured (a moisture content of 20-25 percent) will burn more slowly and produce less creosote. Knocking a log on both sides is a good method of determining the amount of moisture. A damp log will sound dull while seasoned wood will sound sharp.
When the heat produced by a wood fire draws air around it and the smoke and other combustion byproducts are released through the chimney. If the ventilation system in the home isn't adequate it could mean that the chimney is not able to draw enough air and cause an air draft back. This could cause the byproducts of the fire to accumulate inside the house. This could result in an accumulation of dangerous carbon monoxide, as well as flammable creosote and cinders.
Smoke from fires that burn wood can be especially hazardous to people over the age of 65, those with heart or lung diseases as well as children and outdoor woodburning best woodburner stoves - netpinion.Co.kr - enthusiasts. Smoke from wildfires could have a negative impact on the health of older adults, people suffering from heart or lung disease, children and people who are active outdoors.
Safety
There are a few precautions you can take when using a fire that is wood-burning to minimize the risk. You should always use a wood stove or fireplace screen and keep all flammable items at a distance of 3 feet. Smoke and carbon monoxide detectors must also be put in place in your home to alert you when hazardous gases are detected. You should never leave a burning fire unattended, as even a small wall mounted wood burning stove flame can cause an explosive explosion. Also, you should use a metal shovel and the ash bucket to clear ashes from your fireplace or wood stove, and keep it far away from anything flammable.
Lighting the Fire
To start a fire, lay a layer of dry and cut logs on a bed of ash. Then, add a layer of twigs and kindling to the pile. It is crucial to leave enough space between the pieces of wood to allow for airflow. This will prevent the fire from burning too fast. If you need help getting your fire started Try adding a few firelighters to the mix.
Open an opening to let the fire get the oxygen it requires to make it burn brightly. This is particularly important for modern homes, that are often well-insulated and do not have natural draft or ventilation.
After the fire has established, you can add more wood pieces. It is important to remember that even mature hardwoods like oak and hickory can produce plenty of creosote when they are burned.
If possible, only burn kiln-dried or seasoned wood, as this will reduce the possibility of creosote build-up up in your chimney. If you are forced to use green or newly cut firewood, be very careful because it can create more smoke and cause more creosote.
 A wood burning fire can offer a warm and enjoyable experience. However, it can also create harmful combustion products. It is essential to know about the way that wood burns and how to utilize your fireplace.
A wood burning fire can offer a warm and enjoyable experience. However, it can also create harmful combustion products. It is essential to know about the way that wood burns and how to utilize your fireplace.Choose mature logs or kiln dried logs. Logs that are seasoned are less moist and burn hotter than unseasoned logs.
Burning Time
Burning wood to produce heat is a common and efficient method of heating. However, it can release outdoor and indoor emissions that are dangerous to the health of humans. Skillful use of a well-designed fireplace can help reduce the negative effects of burning wood.
The length of time that a wood fire lasts depends on how hot it is. The temperature of the fire will influence the amount of smoke that is produced and the amount of carbon monoxide released. Carbon monoxide can cause occupants to be unable to escape a building that is burning if the levels are too high. It is essential to maintain the temperature of the fire at a lower level the fire to avoid this.
In the initial stage of a wood fire volatile gases such as methane and Methanol are released from the cellulose of the wood. These gases are combustible and non-combustible depending on the moisture levels and the pyrolysis temperature of the sample. The temperature of pyrolysis increases to around 320 degrees Celsius. At this point the cellulose begins to break down and forms charcoal and tar. This process is referred to as wood pyrolysis.
Burning wood releases other toxic combustion products such as dioxins, polyaromatic hydrocarbons, and PAHs. PAHs are known to cause cancer and other illnesses in humans and animals. They can also contaminate soil and water. The wood must be burned in a space that is well ventilated to limit the effects of PAHs.
A wood stove that has an extended burn feature can sustain visible flames for hours while consuming a minimum of fuel. This method of burning involves laying the wood with lighter kindling and larger logs to keep the fire from burning too quickly. This method can be used to achieve the appearance of a fire that produces high temperatures for use over the night or while you are at work.
The duration of a fire is determined by various factors, including the amount of moisture in the wood. Dry wood will have a slower burning time than damp wood. The surface's absorptivity affects its burning time. Simms [59] discovered that the critical heat flux needed to ignite mahogany and oak samples was significantly lower for coated surfaces than those without.
Temperature
The temperature of a fire is incredibly crucial. The temperature of a fire will affect how quickly it burns and also the amount of heat it produces. It also affects the danger when someone is burned. It can also impact how much smoke is produced. If there is a lot of smoke, it can irritate the throat and eyes which is why people should avoid breathing it in.
When wood burns it produces plenty of heat and can even reach high temperatures. The temperature of a fire will differ based on the type of wood that is used and the moisture content. Wet wood, for example is likely to burn at less heat than dry shed wood burning stove. Wet wood absorbs more water, and therefore produces less heat. It is essential to burn dry wood. You should also make sure that the wood has been seasoned before burning.
When the wood reaches a high-burning temperature, a large amount of heat and ash will be released. The amount of ash that is released will be based on the type of wood that is being burned and the heat at which it burns. Certain woods like oak and larch produce very small amounts of ash. The Birch wood can produce a large amount of Ash.
When the wood starts to burn it will go through a three-stage process referred to as pyrolysis. The process begins with the chemical reaction that transforms organic compounds present in the wood into methane and carbon dioxide. The resulting gases are then absorbed by the surrounding air. The gases will rise when the wood is heated and ignite its surface, creating an ignition that heats the wood until it ignites.
The temperature of a fire that is wood burning can be very high, and can cause damage to surfaces if it comes in contact with them. Avoid touching the fire with bare hands as it could cause serious burns. You can reduce your chance of burning by wearing a pair of gloves and working in a well-ventilated area. A mask is recommended when working around fires that burn wood to avoid inhaling smoke.
Smoke
Smoke from wood burning fires is and a mix of gases and fine particles (also known as particulate matter or PM) that contain harmful air pollutants. PM from wood combustion can contain harmful organic compounds, such as formaldehyde and benzene as well mineral particles such as calcium magnesium and potassium. These particles can cause a variety of health problems, including cancer and respiratory diseases. Smoke from wood can cause people to breathe CO, an odorless, colorless gas that can be deadly in small modern wood stove amounts.
The smoke that comes from the wood fire is mostly due to volatile organic compounds (hydrocarbons) evaporating from the burning material. The smoke also contains some water vapor, which is the byproducts of incomplete combustion (such as creosote) as well as some unburned material known as ash.
When choosing the type of wood that you want to burn in your fireplace or woodstove it is recommended to select firewood that has been seasoned. Logs that have been cut and stored away from the weather and allowed to dry until they have been matured (a moisture content of 20-25 percent) will burn more slowly and produce less creosote. Knocking a log on both sides is a good method of determining the amount of moisture. A damp log will sound dull while seasoned wood will sound sharp.
When the heat produced by a wood fire draws air around it and the smoke and other combustion byproducts are released through the chimney. If the ventilation system in the home isn't adequate it could mean that the chimney is not able to draw enough air and cause an air draft back. This could cause the byproducts of the fire to accumulate inside the house. This could result in an accumulation of dangerous carbon monoxide, as well as flammable creosote and cinders.
Smoke from fires that burn wood can be especially hazardous to people over the age of 65, those with heart or lung diseases as well as children and outdoor woodburning best woodburner stoves - netpinion.Co.kr - enthusiasts. Smoke from wildfires could have a negative impact on the health of older adults, people suffering from heart or lung disease, children and people who are active outdoors.
Safety
There are a few precautions you can take when using a fire that is wood-burning to minimize the risk. You should always use a wood stove or fireplace screen and keep all flammable items at a distance of 3 feet. Smoke and carbon monoxide detectors must also be put in place in your home to alert you when hazardous gases are detected. You should never leave a burning fire unattended, as even a small wall mounted wood burning stove flame can cause an explosive explosion. Also, you should use a metal shovel and the ash bucket to clear ashes from your fireplace or wood stove, and keep it far away from anything flammable.
Lighting the Fire
To start a fire, lay a layer of dry and cut logs on a bed of ash. Then, add a layer of twigs and kindling to the pile. It is crucial to leave enough space between the pieces of wood to allow for airflow. This will prevent the fire from burning too fast. If you need help getting your fire started Try adding a few firelighters to the mix.
Open an opening to let the fire get the oxygen it requires to make it burn brightly. This is particularly important for modern homes, that are often well-insulated and do not have natural draft or ventilation.
After the fire has established, you can add more wood pieces. It is important to remember that even mature hardwoods like oak and hickory can produce plenty of creosote when they are burned.
If possible, only burn kiln-dried or seasoned wood, as this will reduce the possibility of creosote build-up up in your chimney. If you are forced to use green or newly cut firewood, be very careful because it can create more smoke and cause more creosote.
- 이전글Responsible For A How To Check The Authenticity Of Pragmatic Budget? 12 Top Ways To Spend Your Money 24.09.22
- 다음글토토사이트추천 【먹튀센터】 메이저사이트 검증사이트 TOP 5 카지노꽁머니 24.09.22
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.