관련뉴스
전문가들이 제공하는 다양한 정보
5 Killer Quora Answers To Mobility Power
작성자 작성자 Carol · 작성일 작성일24-12-28 19:37 · 조회수 조회수 4
페이지 정보
본문
Types of Mobility Power
Many people with disabilities related to mobility benefit from assistive devices, such as braces, canes and crutches as well as wheeled walkers and manual wheelchairs. Certain people with mobility power issues may eventually need to consider power mobility equipment.
A occupational or physical therapist can assess you to determine if a power mobility aid is the right one for you.
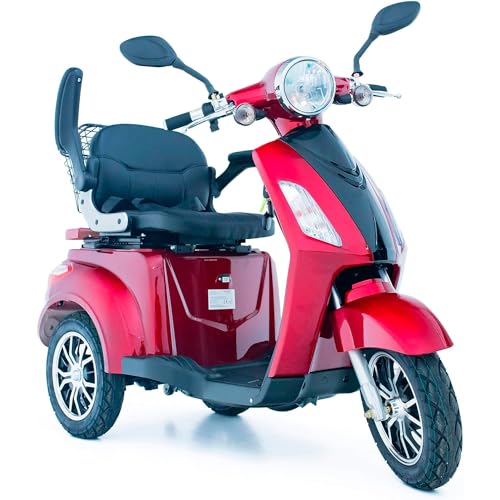
Wheelchairs powered by electricity
Powered wheelchairs provide locomotion for those who are unable to stay upright when using a manual wheelchair. Power wheelchairs are more flexible than scooters. They can be used indoors and outdoors. This lets users cover greater distances. Based on the individual's medical, functional and environmental requirements, therapists can select from a wide variety of configurations for power wheelchairs. Power wheelchairs may include features like a power tilt, power recline, and/or an articulating foot platform to maximize functional independence.
A power wheelchair is typically designed for users to remain upright and use long-lasting rechargeable batteries. The majority of insurance companies will pay the cost of a chair if it is medically required to perform mobility-related daily living activities (MRADLs). Medicare part B covers the majority of power wheelchairs that satisfy certain criteria, including a face-toface appointment with a doctor on the insurer's list, and an evaluation by a physical therapist or occupational therapist.
Certain power wheelchairs have smaller motors, and are designed for indoor use. This allows them to move more easily within small spaces. On the other hand, some power chairs are made to be used indoors as well as outdoors, with larger motors for better grip and precise handling. In order to navigate the outdoors, a lot of power wheelchairs require a special lift on a vehicle in order to be transported.
There are a variety of options and customizations that are available for power wheelchairs, including programmable electronic devices that can control the speed of the motors and track systems to assist the chair in maintaining an even path over uneven terrain and other upgrades. Some power wheelchairs offer a tilt-in space option for users that cannot remain upright for long periods of time. This can help relieve pressure points and improve circulation.
Some power wheelchairs come with removable components, such as the battery and motors to make transportation easier. Some have a folding frame for storage in the back of a car or van. Some medical supply stores offer the possibility of renting a chair prior to buying one. The cost of renting is often credited towards the purchase price.
Scooters Powered by Electric Motors
Powered scooters provide an easy and quiet ride. They are often smaller than motorbikes, and are suitable for people with weak upper body strength or severe accessibility needs. They are also easier to store, and more mobile than a wheelchair. They are popular with kids and teens since they can be used to travel short or medium distances.
As opposed to power wheelchairs scooters can be driven using either hand. They typically have a step-through frame and a handlebar set-up to control. A small battery powers a motor at the deck's base. The motor can be chain or direct driven, depending on the scooter.
The best electric scooters are designed for various abilities and environments. Some of the best-rated models are capable of reaching speeds of up to 15mph on flat, stable surfaces. Others can drive for up to 10 miles on one charge. These scooters are ideal for those who are able to walk short distances but need help navigating hills, steps or uneven terrain.
Many electric scooters feature a "grip-twist" throttle, which requires the user to press down a button on the handlebar or a light gray rotating piece. This ensures the motor always gets power and also prevents children from slipping their hands off and causing a sudden and sharp shock. Several models also incorporate an additional safety mechanism referred to as "kick to start" which requires the child to get the scooter moving before the motor kicks in.
Some scooters feature a simple chain reduction drive that allows the motor's spindle to be directly connected to the rear wheel. This is a common type of scooter, especially among youngsters, as it allows the rider to easily get up to speed without having to pedal.
Other scooters utilize an electronic controller that converts inputs from the accelerator and brake controls into current that is sent to the motor. This is known as a speed control and is different from model to model. It's essential to find a scooter with a high-quality speed controller that is suitable for the purpose of.
Bicycles that are powered
E-bikes provide a convenient, healthy, low-carbon alternative to auto transportation, and may provide an increase in mobility for those who have physical limitations. While traditional bicycles rely on human power, e-bikes include an electric motor in that helps you pedal and allows you to travel further and climb hills without exhaustion. Every major bike maker and even car manufacturers are now involved in the e-bike market making bikes that meet the needs of a diverse range of riders.
The most common e-bike design includes a motor within the frame, in the cranks or hubs at the front or back. The motor drives the wheel via the chain or gears. You can choose from a range of settings to determine how much assistance you get. The motor has a torque sensor which can detect your pedaling efforts and adjust accordingly. This means you receive more power when pedal hard, and less when you don't.
Pedal Assist Mode
Many e-bikes come with several modes that allow you to alter the amount of power the motor produces. In class 1 mode, the motor provides power when you're pedaling, making cycling effortless and allowing you to ride farther and climb hills with ease. In class 2 mode, the motor supplies green power mobility at a constant level, while in class 3 mode, you can use the throttle to reach speeds up to 28 mph.
E-bikes are not without their challenges. Environmentalists are concerned about the carbon emissions and resource depletion that could result from the manufacture of electronic bikes, while trail enthusiasts are concerned about the effect the e-bikes can have on natural trails. Some are concerned about safety, especially the risk of accidents if bikes share the road with traditional bikes.
To reduce these risks, policymakers should implement changes to improve the safety and sustainability e-bikes. For instance, requiring e-bikes to meet strict battery safety standards can help reduce the risk of fires and explosions. In addition, offering E-bike safety training and incorporating e-bikes into public education programs can promote awareness of the dangers of riding bikes and help ensure that users know how to operate these vehicles safely.
Vehicles Powered by Electric Power
Powered vehicles (EVs) use an electric motor to drive the wheels of the vehicle. They can operate on pure electricity, which could come from batteries or a fuel cell, or be hybrid electric vehicles that make use of both an internal combustion engine and an electric motor. Other types of EVs are bicycles and battery electric scooters electric vehicles for the neighborhood (like golf carts) forklifts, and utility/commercial cars like milk floats or transit buses.
EVs are the future for transportation, and are already becoming more popular. According to McKinsey Global EV sales will double from 2021 until 2030. To sustain this growth governments and companies must answer several questions, including:
How can we cleanly power EVs?
Unlike fossil-fuel vehicles, EVs don't emit harmful emissions from their tailpipes. They still depend on the grid for charging, which is a major problem as the energy sector moves towards renewables. As EVs become more common and more widespread, they will require faster and more frequent charging, putting pressure on the grid infrastructure.
In order to improve mobility, more charging stations are needed. These stations--also known as EV charge points charging point, chargerpoint, or electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE)--convert DC power with high voltage into DC power of lower voltage to recharge batteries in EVs. This power can be used to operate vehicle accessories and power the motor for traction.
An EV's traction motor is a powerful electric motor that is the motor that drives the wheels of the vehicle. The traction battery pack is used to generate energy. It can be charged externally or internally. The traction battery is comprised of modules that contain numerous smaller cells. These modules are connected in parallel and create a larger unit. The system's chemistry and sensors constantly monitor and balance the pack to ensure that it is operating at its best.
 Plug-in electric vehicles, also known as HEVs, combine the advantages of gas engines and an electric motor. They are able to travel short distances with electricity, but only at higher speeds. They use a variety of hybrid functions, including idle-start-stop technology as well as engine green power electric mobility scooter-assist and brakes that regeneratively work. Mild HEVs can make use of all hybrid vehicle technologies. However, large or full-sized HEVs can only drive with the motors for traction.
Plug-in electric vehicles, also known as HEVs, combine the advantages of gas engines and an electric motor. They are able to travel short distances with electricity, but only at higher speeds. They use a variety of hybrid functions, including idle-start-stop technology as well as engine green power electric mobility scooter-assist and brakes that regeneratively work. Mild HEVs can make use of all hybrid vehicle technologies. However, large or full-sized HEVs can only drive with the motors for traction.
Many people with disabilities related to mobility benefit from assistive devices, such as braces, canes and crutches as well as wheeled walkers and manual wheelchairs. Certain people with mobility power issues may eventually need to consider power mobility equipment.
A occupational or physical therapist can assess you to determine if a power mobility aid is the right one for you.
Wheelchairs powered by electricity
Powered wheelchairs provide locomotion for those who are unable to stay upright when using a manual wheelchair. Power wheelchairs are more flexible than scooters. They can be used indoors and outdoors. This lets users cover greater distances. Based on the individual's medical, functional and environmental requirements, therapists can select from a wide variety of configurations for power wheelchairs. Power wheelchairs may include features like a power tilt, power recline, and/or an articulating foot platform to maximize functional independence.
A power wheelchair is typically designed for users to remain upright and use long-lasting rechargeable batteries. The majority of insurance companies will pay the cost of a chair if it is medically required to perform mobility-related daily living activities (MRADLs). Medicare part B covers the majority of power wheelchairs that satisfy certain criteria, including a face-toface appointment with a doctor on the insurer's list, and an evaluation by a physical therapist or occupational therapist.
Certain power wheelchairs have smaller motors, and are designed for indoor use. This allows them to move more easily within small spaces. On the other hand, some power chairs are made to be used indoors as well as outdoors, with larger motors for better grip and precise handling. In order to navigate the outdoors, a lot of power wheelchairs require a special lift on a vehicle in order to be transported.
There are a variety of options and customizations that are available for power wheelchairs, including programmable electronic devices that can control the speed of the motors and track systems to assist the chair in maintaining an even path over uneven terrain and other upgrades. Some power wheelchairs offer a tilt-in space option for users that cannot remain upright for long periods of time. This can help relieve pressure points and improve circulation.
Some power wheelchairs come with removable components, such as the battery and motors to make transportation easier. Some have a folding frame for storage in the back of a car or van. Some medical supply stores offer the possibility of renting a chair prior to buying one. The cost of renting is often credited towards the purchase price.
Scooters Powered by Electric Motors
Powered scooters provide an easy and quiet ride. They are often smaller than motorbikes, and are suitable for people with weak upper body strength or severe accessibility needs. They are also easier to store, and more mobile than a wheelchair. They are popular with kids and teens since they can be used to travel short or medium distances.
As opposed to power wheelchairs scooters can be driven using either hand. They typically have a step-through frame and a handlebar set-up to control. A small battery powers a motor at the deck's base. The motor can be chain or direct driven, depending on the scooter.
The best electric scooters are designed for various abilities and environments. Some of the best-rated models are capable of reaching speeds of up to 15mph on flat, stable surfaces. Others can drive for up to 10 miles on one charge. These scooters are ideal for those who are able to walk short distances but need help navigating hills, steps or uneven terrain.
Many electric scooters feature a "grip-twist" throttle, which requires the user to press down a button on the handlebar or a light gray rotating piece. This ensures the motor always gets power and also prevents children from slipping their hands off and causing a sudden and sharp shock. Several models also incorporate an additional safety mechanism referred to as "kick to start" which requires the child to get the scooter moving before the motor kicks in.
Some scooters feature a simple chain reduction drive that allows the motor's spindle to be directly connected to the rear wheel. This is a common type of scooter, especially among youngsters, as it allows the rider to easily get up to speed without having to pedal.
Other scooters utilize an electronic controller that converts inputs from the accelerator and brake controls into current that is sent to the motor. This is known as a speed control and is different from model to model. It's essential to find a scooter with a high-quality speed controller that is suitable for the purpose of.
Bicycles that are powered
E-bikes provide a convenient, healthy, low-carbon alternative to auto transportation, and may provide an increase in mobility for those who have physical limitations. While traditional bicycles rely on human power, e-bikes include an electric motor in that helps you pedal and allows you to travel further and climb hills without exhaustion. Every major bike maker and even car manufacturers are now involved in the e-bike market making bikes that meet the needs of a diverse range of riders.
The most common e-bike design includes a motor within the frame, in the cranks or hubs at the front or back. The motor drives the wheel via the chain or gears. You can choose from a range of settings to determine how much assistance you get. The motor has a torque sensor which can detect your pedaling efforts and adjust accordingly. This means you receive more power when pedal hard, and less when you don't.
Pedal Assist Mode
Many e-bikes come with several modes that allow you to alter the amount of power the motor produces. In class 1 mode, the motor provides power when you're pedaling, making cycling effortless and allowing you to ride farther and climb hills with ease. In class 2 mode, the motor supplies green power mobility at a constant level, while in class 3 mode, you can use the throttle to reach speeds up to 28 mph.
E-bikes are not without their challenges. Environmentalists are concerned about the carbon emissions and resource depletion that could result from the manufacture of electronic bikes, while trail enthusiasts are concerned about the effect the e-bikes can have on natural trails. Some are concerned about safety, especially the risk of accidents if bikes share the road with traditional bikes.
To reduce these risks, policymakers should implement changes to improve the safety and sustainability e-bikes. For instance, requiring e-bikes to meet strict battery safety standards can help reduce the risk of fires and explosions. In addition, offering E-bike safety training and incorporating e-bikes into public education programs can promote awareness of the dangers of riding bikes and help ensure that users know how to operate these vehicles safely.
Vehicles Powered by Electric Power
Powered vehicles (EVs) use an electric motor to drive the wheels of the vehicle. They can operate on pure electricity, which could come from batteries or a fuel cell, or be hybrid electric vehicles that make use of both an internal combustion engine and an electric motor. Other types of EVs are bicycles and battery electric scooters electric vehicles for the neighborhood (like golf carts) forklifts, and utility/commercial cars like milk floats or transit buses.
EVs are the future for transportation, and are already becoming more popular. According to McKinsey Global EV sales will double from 2021 until 2030. To sustain this growth governments and companies must answer several questions, including:
How can we cleanly power EVs?
Unlike fossil-fuel vehicles, EVs don't emit harmful emissions from their tailpipes. They still depend on the grid for charging, which is a major problem as the energy sector moves towards renewables. As EVs become more common and more widespread, they will require faster and more frequent charging, putting pressure on the grid infrastructure.
In order to improve mobility, more charging stations are needed. These stations--also known as EV charge points charging point, chargerpoint, or electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE)--convert DC power with high voltage into DC power of lower voltage to recharge batteries in EVs. This power can be used to operate vehicle accessories and power the motor for traction.
An EV's traction motor is a powerful electric motor that is the motor that drives the wheels of the vehicle. The traction battery pack is used to generate energy. It can be charged externally or internally. The traction battery is comprised of modules that contain numerous smaller cells. These modules are connected in parallel and create a larger unit. The system's chemistry and sensors constantly monitor and balance the pack to ensure that it is operating at its best.
 Plug-in electric vehicles, also known as HEVs, combine the advantages of gas engines and an electric motor. They are able to travel short distances with electricity, but only at higher speeds. They use a variety of hybrid functions, including idle-start-stop technology as well as engine green power electric mobility scooter-assist and brakes that regeneratively work. Mild HEVs can make use of all hybrid vehicle technologies. However, large or full-sized HEVs can only drive with the motors for traction.
Plug-in electric vehicles, also known as HEVs, combine the advantages of gas engines and an electric motor. They are able to travel short distances with electricity, but only at higher speeds. They use a variety of hybrid functions, including idle-start-stop technology as well as engine green power electric mobility scooter-assist and brakes that regeneratively work. Mild HEVs can make use of all hybrid vehicle technologies. However, large or full-sized HEVs can only drive with the motors for traction.- 이전글Why Tilt And Turn Window Adjustment Isn't A Topic That People Are Interested In. 24.12.28
- 다음글You'll Be Unable To Guess Best Crypto Online Casino's Secrets 24.12.28
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.